Describe the Three Types of Vesicles.
Three kinds of coated vesicles which appear to function in different types of vesicular transport have been characterized. Exocytotic vesicles are formed by the Golgi apparatus endosomes and pre-synaptic neurons.
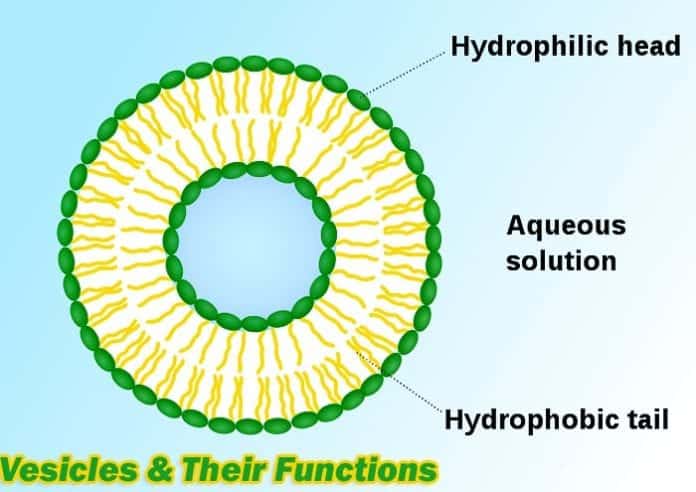
Vesicle Functions Types Of Vesicles 9 Major Functions Of Vesicles
Material is enclosed by in folding of plasma membrane called a coated pit.
. Biology 22062019 0750 waves2114. - 458192 Roloff664 Roloff664 05132015 Biology High School answered Describe three types of vesicles. It is rather just like exocytosis and endocytosis.
3 fundamental actions associated with this process are. All cells make proteins and require them to function. Coated vesicles are divided into three categories based on their coat proteins.
Apocrine 3 The one that involves bursting of the gland and. I vesicle formation ii vesicle transportation and iii docking in the cell. There are essentially four types of vesicles used by cells.
There are three primary types of endocytosis. Merocrine 2 The one that loses cytoplasm with its secretion is. Add your answer and earn points.
This essay is going to describe three different types of brain-imaging techniques. The first to be described were the clathrin -coated vesicles which are responsible for the uptake of extracellular molecules from the plasma membrane by endocytosis see Chapter 12 as well as the transport of molecules. Indeed polymerization of the triskelions is believed to form the pit deepening it and eventually freeing it from the membrane as a small coated vesicle.
Exocytosis is the process of secreting proteins from a cell into the medium by transport in membranous. Describe the nature of our understanding of the different types of coated vesicles Three major types of coated vesicles have been characterized each with a different type of protein coat and each formed by reversible polymerization of a distinct set of protein subunits. Coated vesicles are vesicles whose membrane has on its surface a layer of a protein such as clathrin cop-I or COP-II.
Types of Vesicles. The vesicle is pinched off from the membrane as the ends of the in-folded membrane fuse together. 100 2 ratings Answer 1 The type of secretion that uses vesicles and loses no cytoplasm is.
Secretory vesicles include synaptic vesicles and vesicles in endocrine tissues. Vesicular transport within the cell is called transcytosis or cytopempsis. These are off three types.
Vesicle detaches from membrane. The three types of brain-imaging techniques that will be clearly described are. Transport vesicles move molecules within the cells.
Dense tufts- these are filamentous projections present close to the vesicles. Steps of exocytosis include vesicle trafficking tethering docking priming and fusing. Vesicle fuses with endosome for processing and sorting.
Second is the second class includes wags says Third is the third class that includes lipids usually without Easter groups such as steroids. Clathrin-coated COPI-coated and COPII-coated vesicles Figure 13-4. COPI- and COPII-coated vesicles for example facilitate transport between the ER and the Golgi cisternae whereas Clathrin-coated vesicles mediate transport from the Golgi apparatus and.
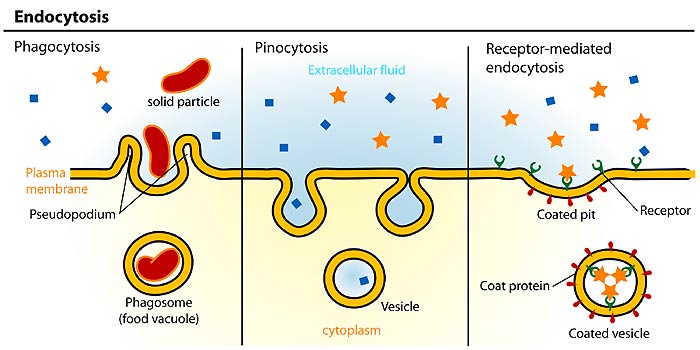
Start your trial now. Phagocytosis pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis. The internalized vesicle is then processed by the cell.
Clathrin-coated COPI-coated and COPII-coated vesicles. Describe three types of vesicles. Enumerate the three types of coat proteins and describe the characteristics of the vesicles that they are associated with.
There are three well-characterized types of coated vesicles which differ in their coat proteins. Name each of the three primary embryonic brain vesicles. They are of three types of small vesicles with clear code small vesicles with dense code and large vesicles with a dense core.
They are vacuoles lysosomes transport vesicles and secretory vesicles. Each type is used for different transport steps in the cell. It will also explain what the literature tells us about the function and the structure of the brain.
May recycle back components to the membrane. Enumerate the three types of coat proteins and describe the characteristics of the vesicles that they are associated with. The clathrins subunits molecular weight about 180000 occur in three-armed trimers called triskelions that interact with one another to form a cage like net around the pit.
First week only 499. Secretory vesicles contain materials that are to be excreted from the cell such as wastes or hormones. Which was most likely an effect on society that resulted from improvements in blood handling during world war i and world war ii.
View the full answer. Vacuoles are vesicles that contain mostly water. Endocytosis is process by which proteins at the surface of the cell are internalized being transported into the cell within membranous vesicles.
In the cell each kind is used for a distinct transit stage. Another type os vesicles that do not originate from the Golgi complexes are those found on the synaptic terminals of the neurons. The transport vesicles then bud off from the early endosome transporting the proteins and lipids to the cell membrane and waste materials to the lysosomes where they are degraded.
Synaptic vesicles -they contain neurotransmitters like acetylcholine gamma-aminobutyric acid glycine catecholamines neuropeptides etc. Three pathways of exocytosis are constitutive exocytosis regulated exocytosis and lysosome mediated exocytosis. 1 See answer Roloff664 is waiting for your help.
1 Get Other questions on the subject. Describe three types of vesicles. First is the first class and this includes oils fat and forceful lipids.
Describe three types of vesicles.

Three Types Of Endocytosis Receptor Mediated Pinocytosis And Phagocytosis Plasma Membrane Human Anatomy And Physiology Science Notes
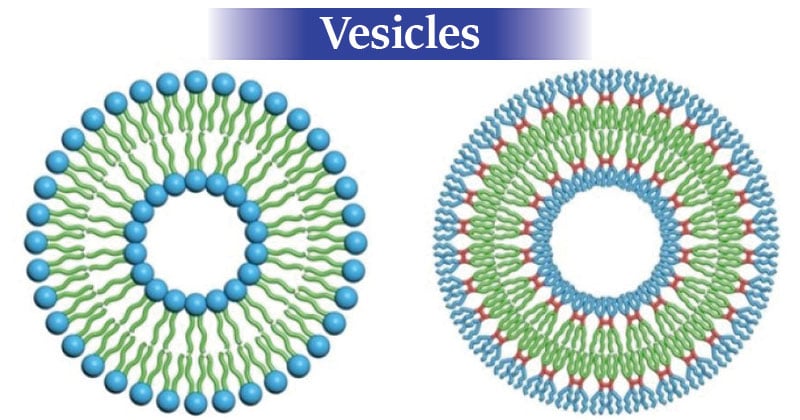
Vesicles Definition Structure Functions And Diagram

Vesicle Functions Types Of Vesicles 9 Major Functions Of Vesicles
No comments for "Describe the Three Types of Vesicles."
Post a Comment